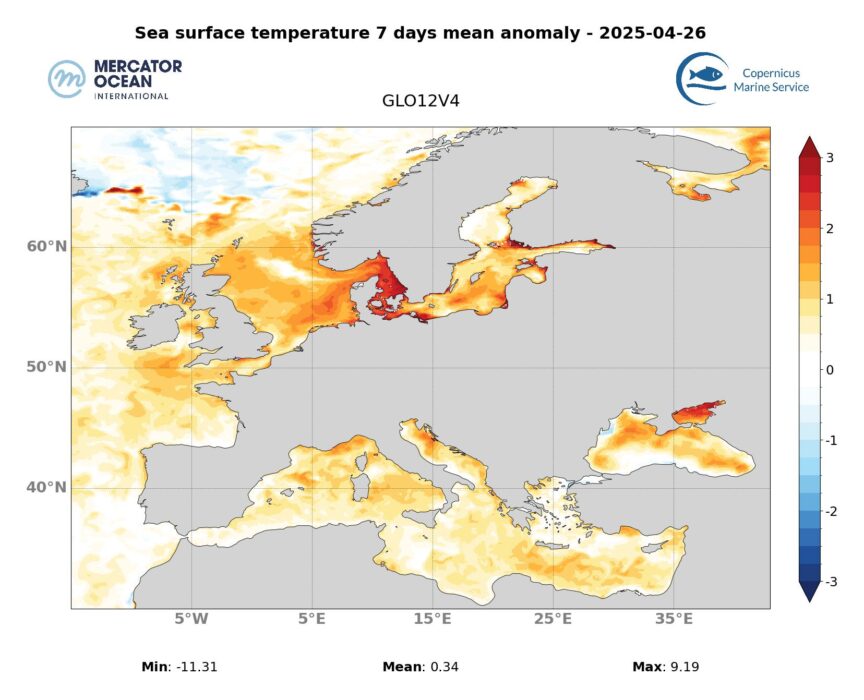
The marine heatwave bulletin provides forecasts and analysis of marine heatwave events across the globe and throughout the year. Used datasets include observations (satellite sea surface temperature maps) and numerical model analyses (assimilating satellite and in situ observations) to derive marine heatwave forecasts for a 10-day period. This week’s forecasts were produced using as a comparison the marine heatwave situation on 15/04/2025.
Forecasts for 26 April
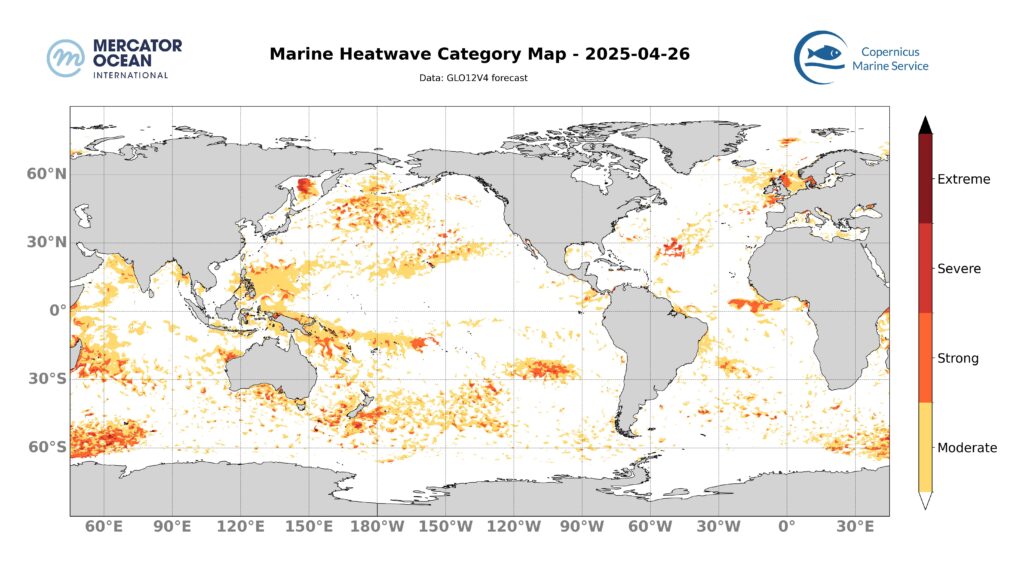
Tropical Atlantic Ocean
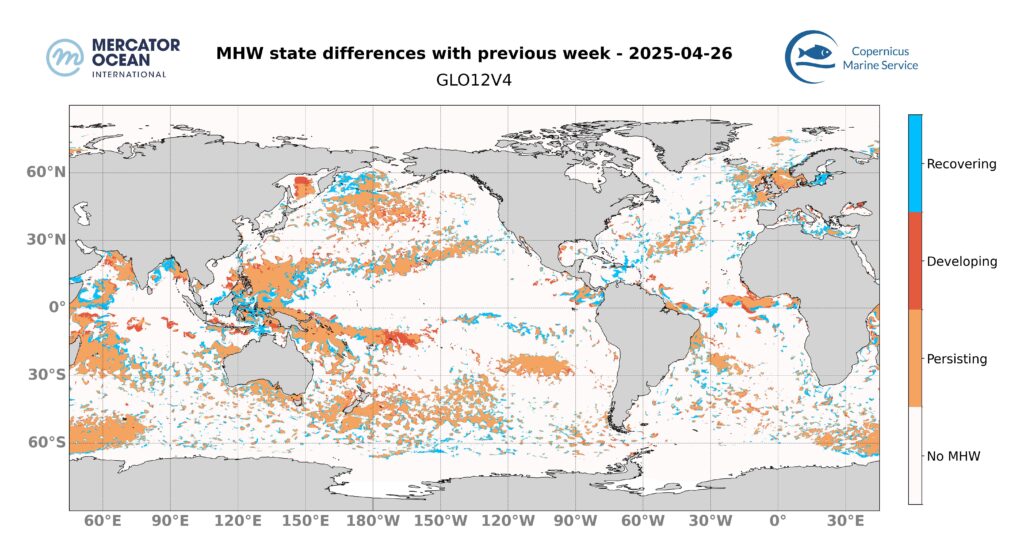
The marine heatwave in the tropical Atlantic Ocean dispersed and only a few scattered areas remain in moderate category. At 60°W the marine heatwave increases in intensity with strong category. Towards the equator and off the coast of Africa, the moderate to locally strong marine heatwave is intensifying with strong category.
Tropical Pacific Ocean
The marine heatwave from the north of Indonesia to the west of Papua New Guinea decreases in intensity with moderate category. The marine heatwave in the centre of the basin at around 20°N and at 30°S and 110°W, remains stable.
Indian Ocean
In the Bay of Bengal and in the Arabian Sea, the extent and intensity of marine heatwaves are decreasing with moderate category. Off the coast of Madagascar, the marine heatwave remains stable.
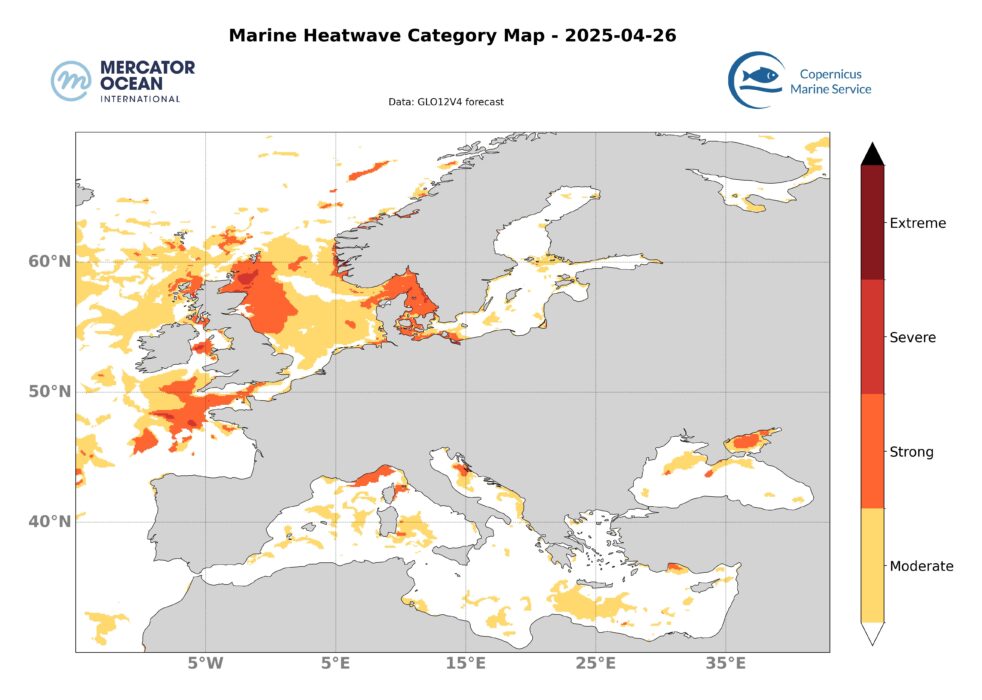
European Zone
North Atlantic Ocean
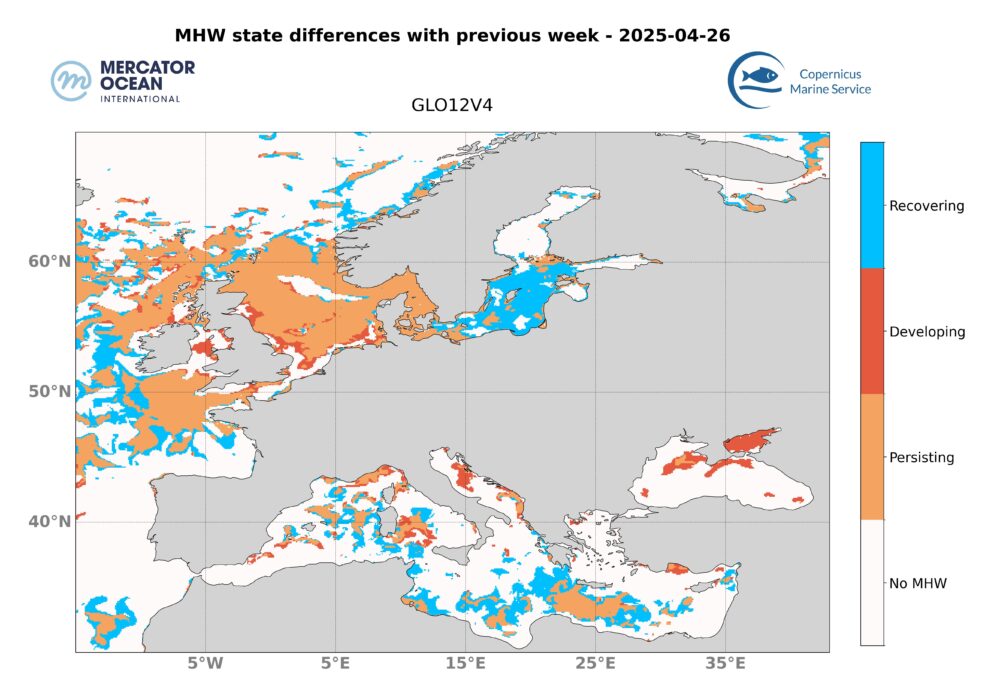
The marine heatwave off Breton coast, off Scottish coast and in the Strait of Skagerrak and Kattegat increases in intensity with strong to locally sever categories and decreases in extent.
Mediterranean Sea
The marine heatwave in the Mediterranean basin is decreasing, and only a few scattered areas remain in moderate category.
Weekly Temperature Anomalies
20 – 26 April 2025
| Mediterranean Sea | 0.5°C to 1.5°C |
| Tropical Pacific Ocean | -1°C to 2°C |
| North Atlantic Ocean | -3°C à 3°C |
| Tropical Atlantic Ocean | -1°C to 1°C |
| Indian Ocean | 0°C to 2°C |
Access the Daily Global Physical Bulletin for a 9-day forecast here.
SURVEY
Help us improve our content! Answer a quick survey about this bulletin here.
What are marine heatwaves?
Marine heatwaves (MHW) are extreme rises in ocean temperature for an extended period of time. They can occur at different locations in the ocean, and their magnitude and frequency have increased over the last couple of decades, with harmful impacts on ecosystems, and human activities. According to the latest report released by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC AR6 SYR), it is found with high confidence that in the near-term at 1.5°C global warming, the increasing frequency of marine heatwaves will increase risks of biodiversity loss in the oceans, including from mass mortality events.
How are marine heatwaves calculated?
A marine heatwave is an episode during which the ocean temperature is abnormally warm for at least 5 consecutive days.
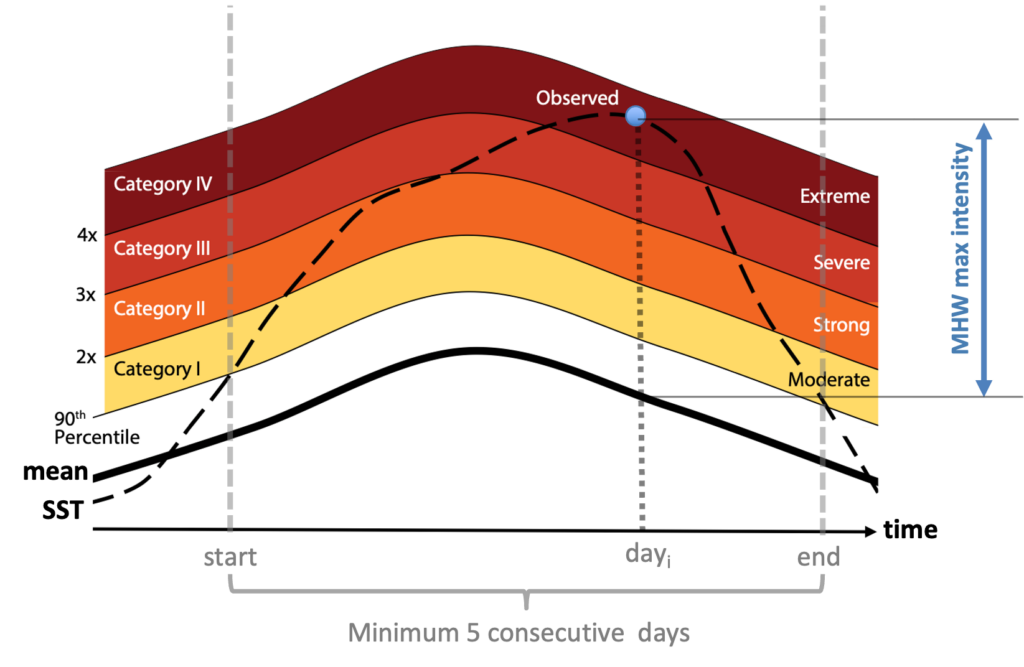
Adapted from Hobday et al. (2018)
For any location in the ocean, the normal temperatures are defined for every day of the year using a climatological period (here 1993–2016). A heatwave is identified when the measured daily temperature is within the top 10% of the highest recorded values for that day (i.e., above the 90th percentile, see diagram), and with this condition persisting for at least five consecutive days.
The intensity of the heatwave on any given day is measured as the number of degrees above the climatological average (represented by the bold black line) indicated by the blue arrow. We can either calculate the cumulative intensity over the entire heatwave or record the maximum intensity.
Heatwaves are classified based on their intensity level. To do this, the intensity is compared to the difference between the climatological value and the 90th percentile value. A mhw intensity between 1 and 2 times this difference corresponds to a heatwave of moderate category; between 2 and 3 times, to a strong category; between 3 and 4 times, to a severe category; and a difference greater than 4 times corresponds to an extreme category.
Notes
Datasets and products :
Global Ocean Physics Analysis and Forecast (sea surface temperature) E.U. Copernicus Marine Service/ Mercator Ocean International. https://doi.org/10.48670/moi-00016
IPCC AR6 SYR chapter 4.3 https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar6/syr/downloads/report/IPCC_AR6_SYR_LongerReport.pdf