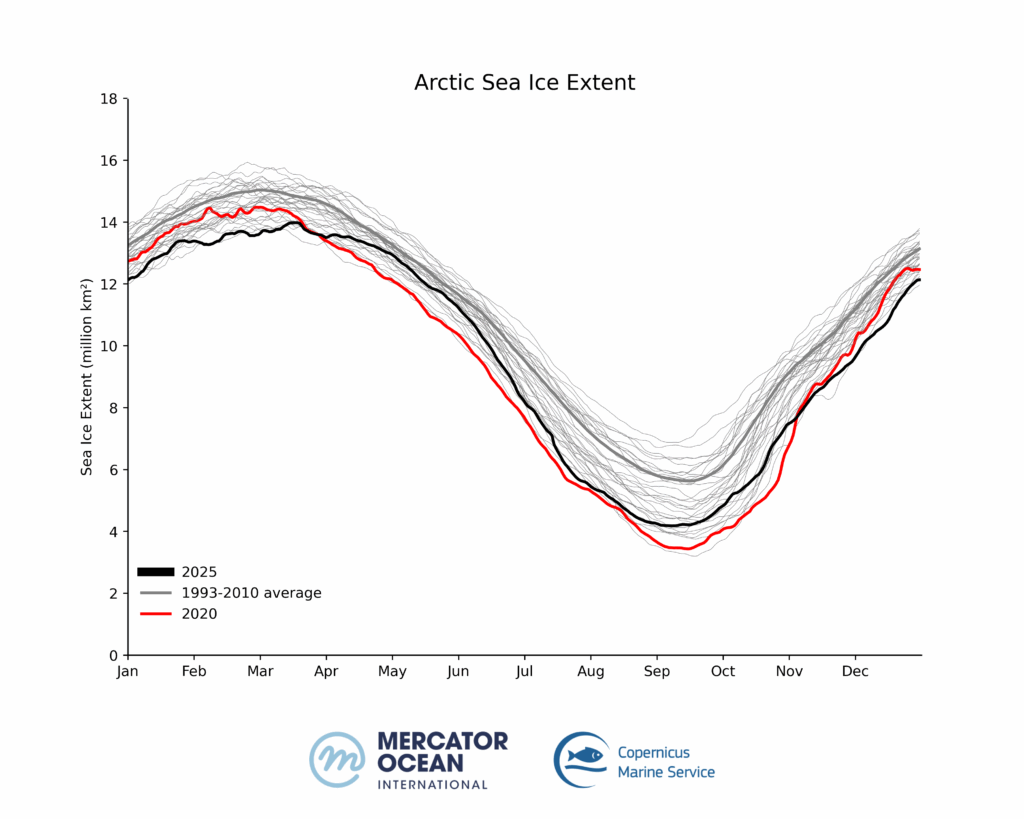
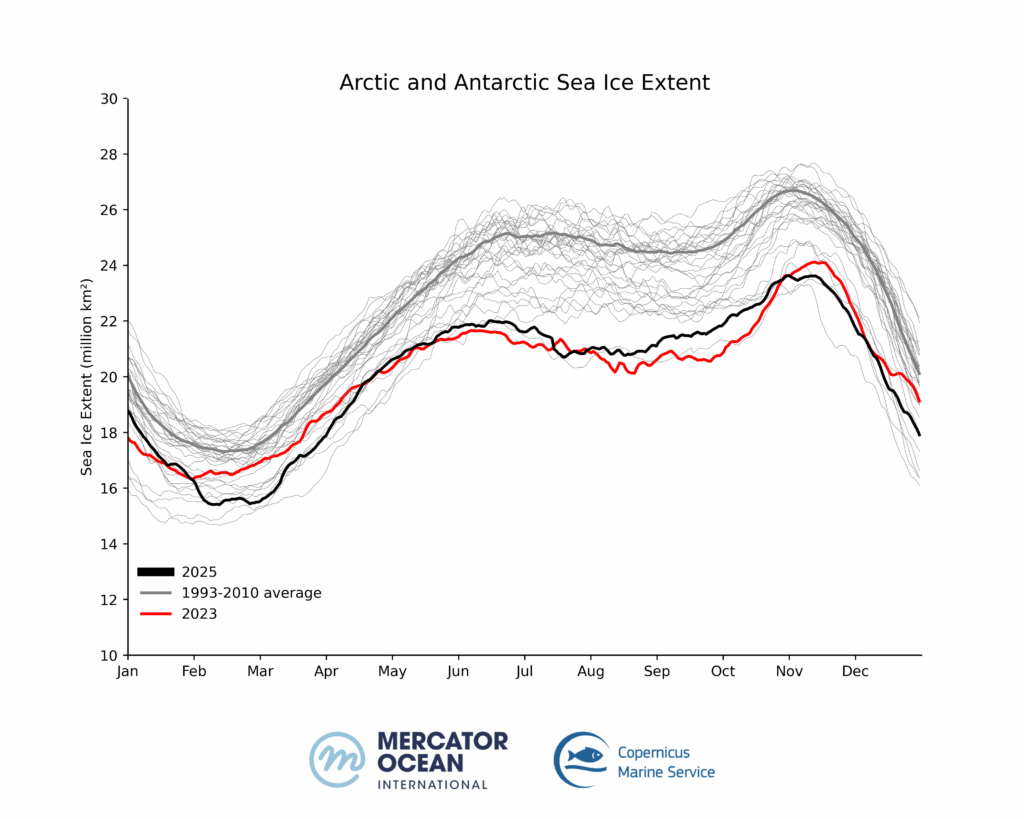
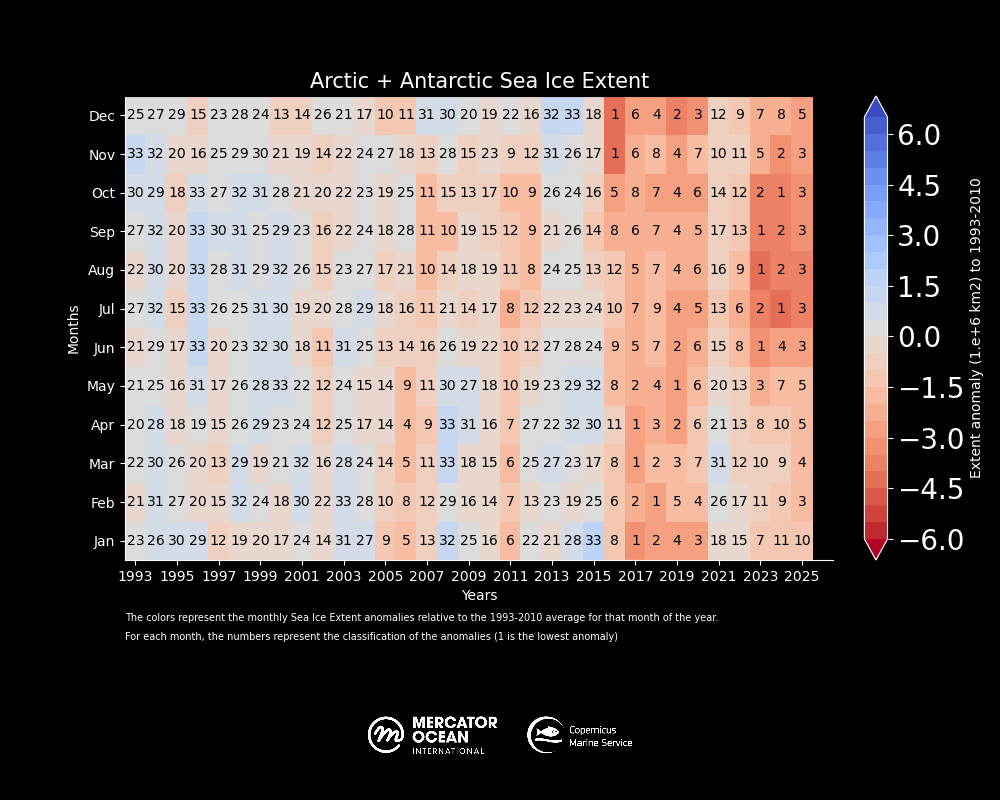
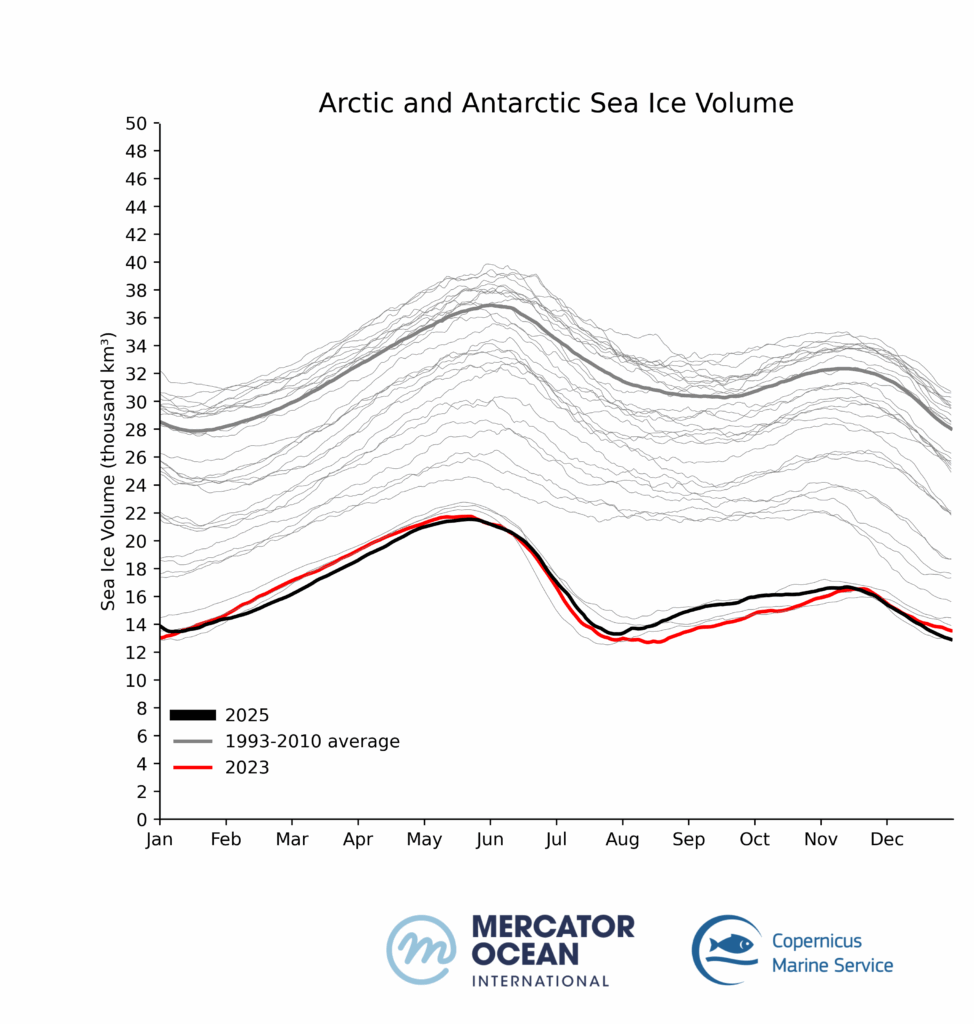
Sea ice cover in the Arctic registered among the 3 lowest winter values during the first trimester of 2025. By September, at the end of the summer in the Northern Hemisphere, sea ice remained as low as the 7th lowest.
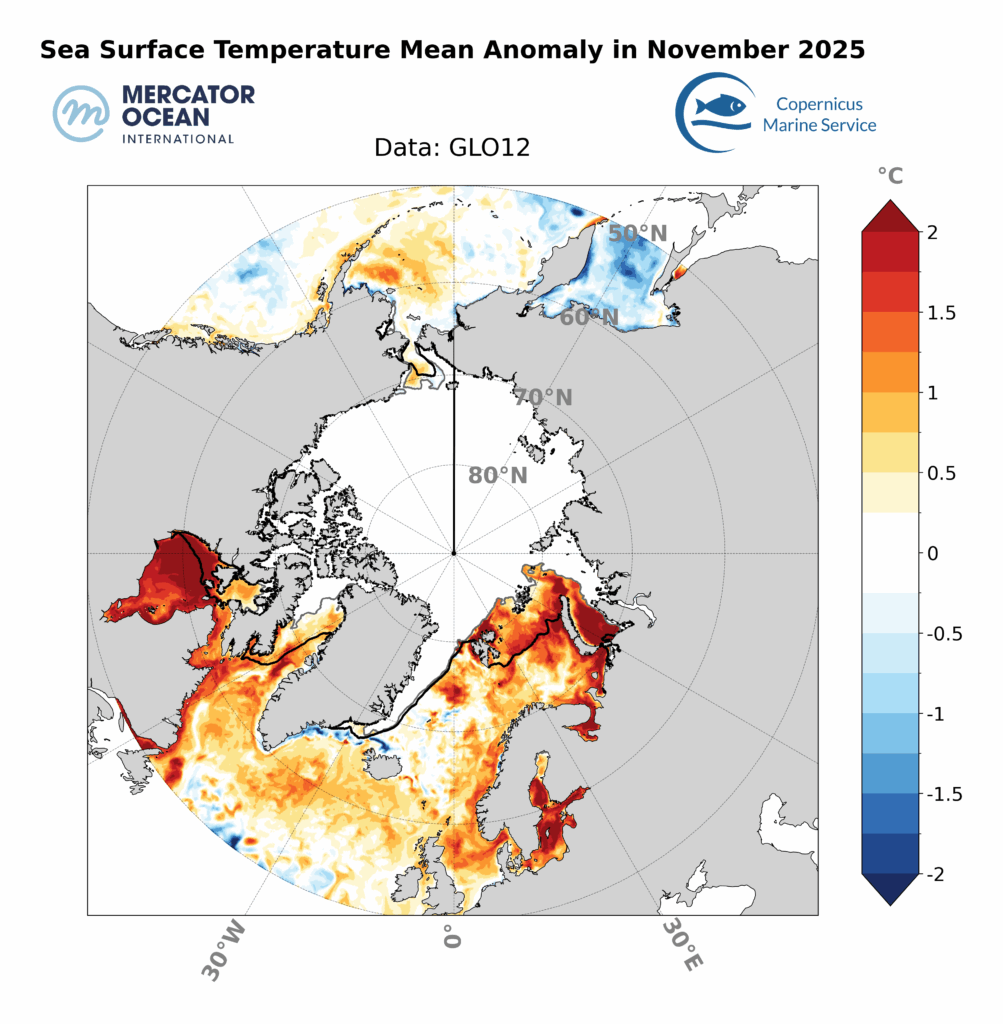
Entering November 2025, the formation of sea ice remained very low for the season below the long-term average of 1993-2010) and as the second lowest for this month after 2016. December 2025 reached record low sea ice values in the region.
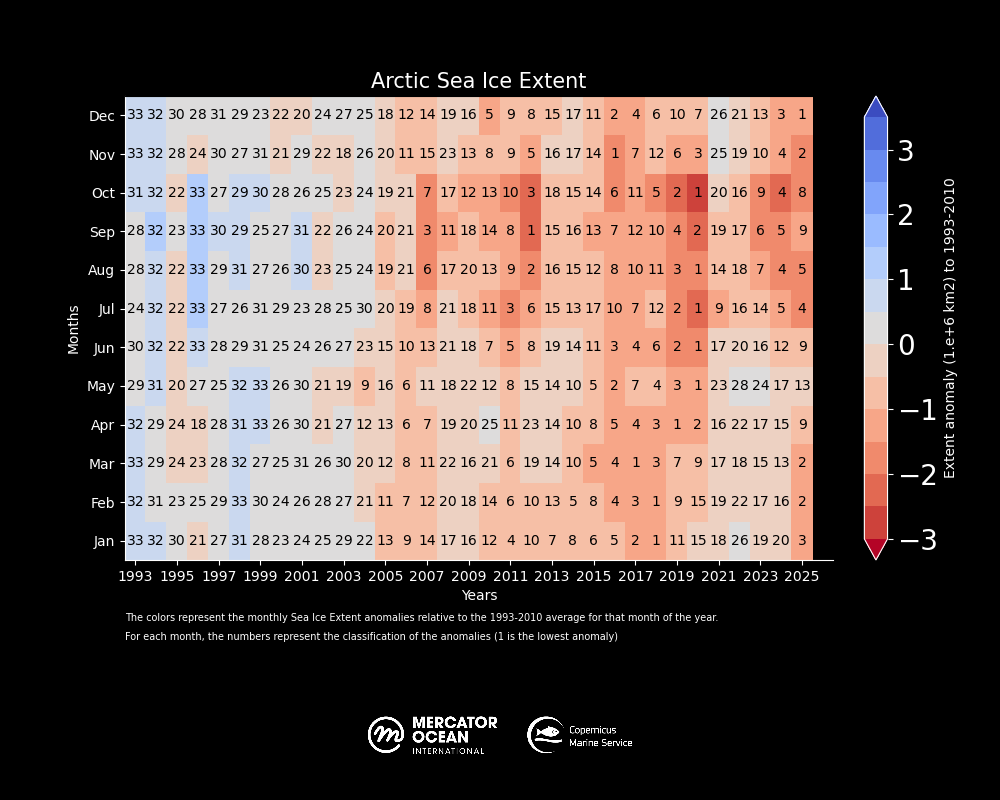
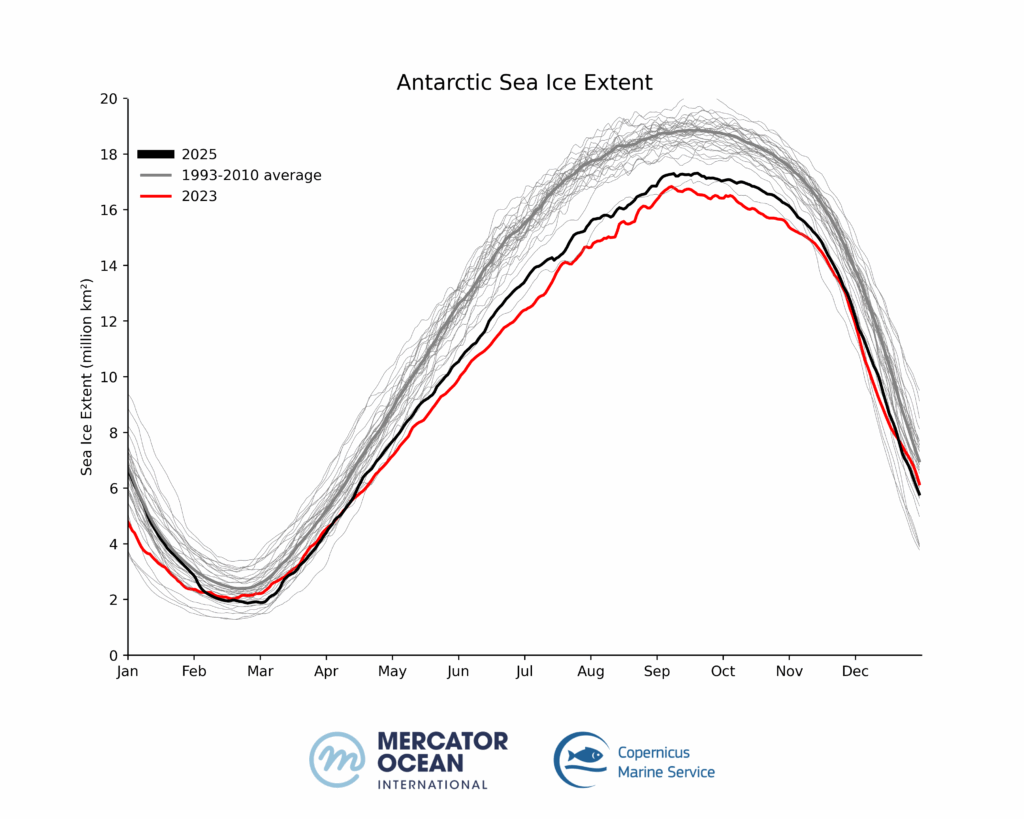
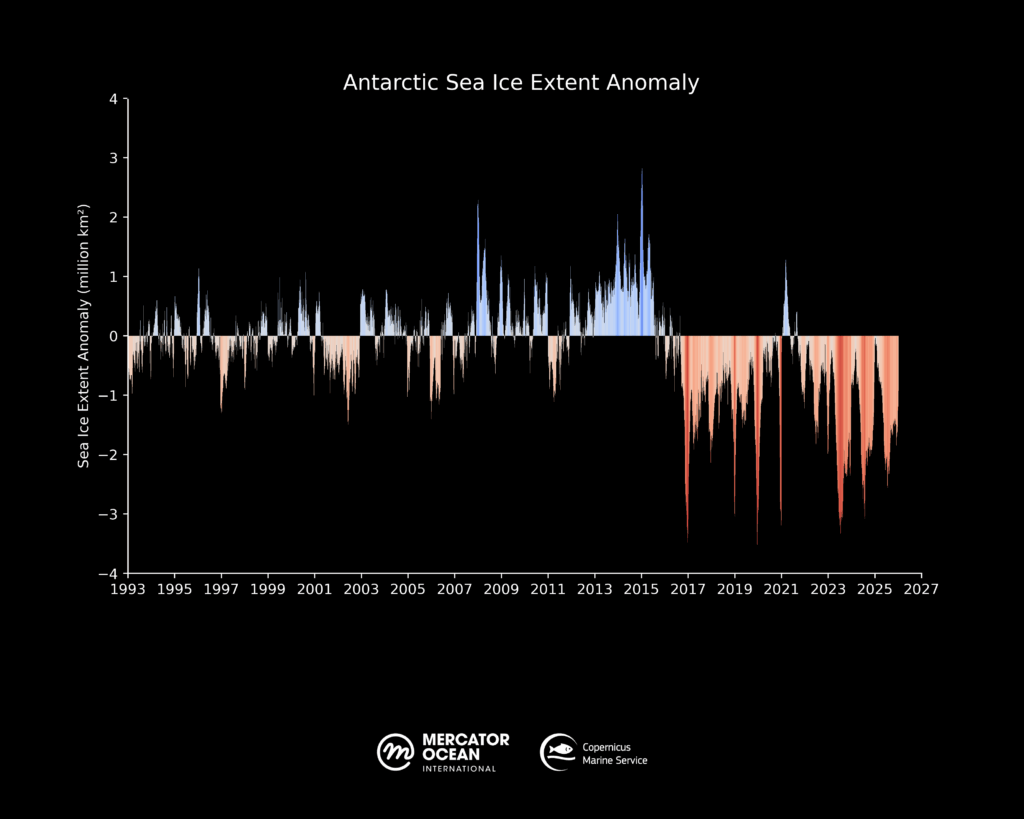
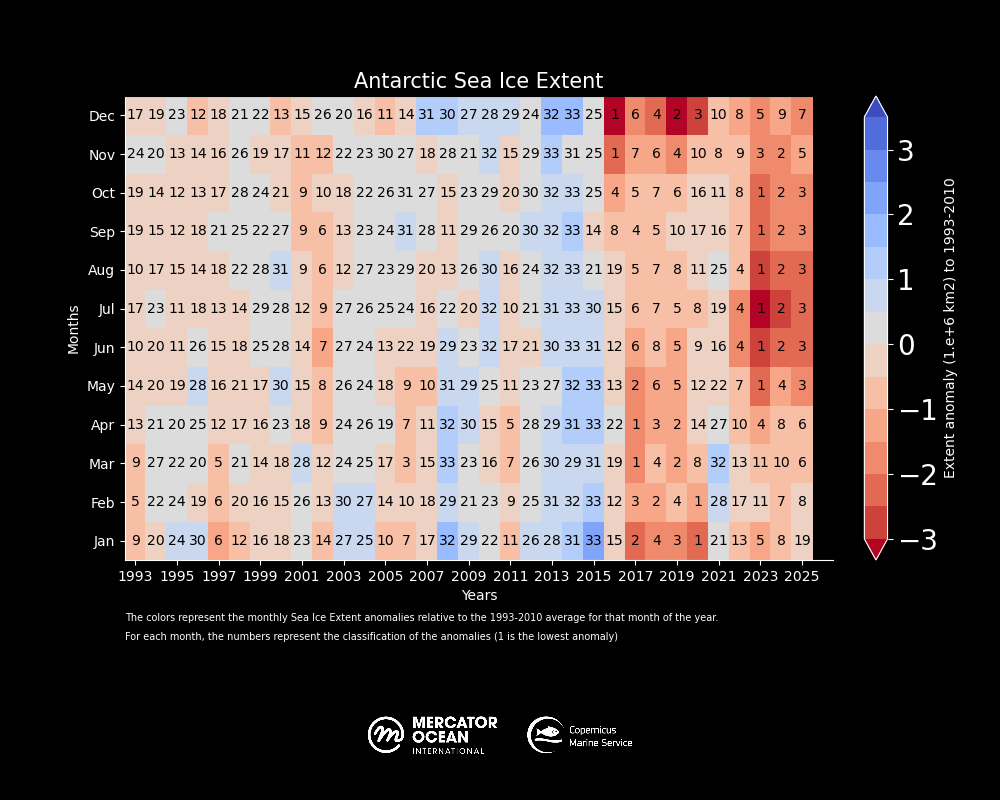
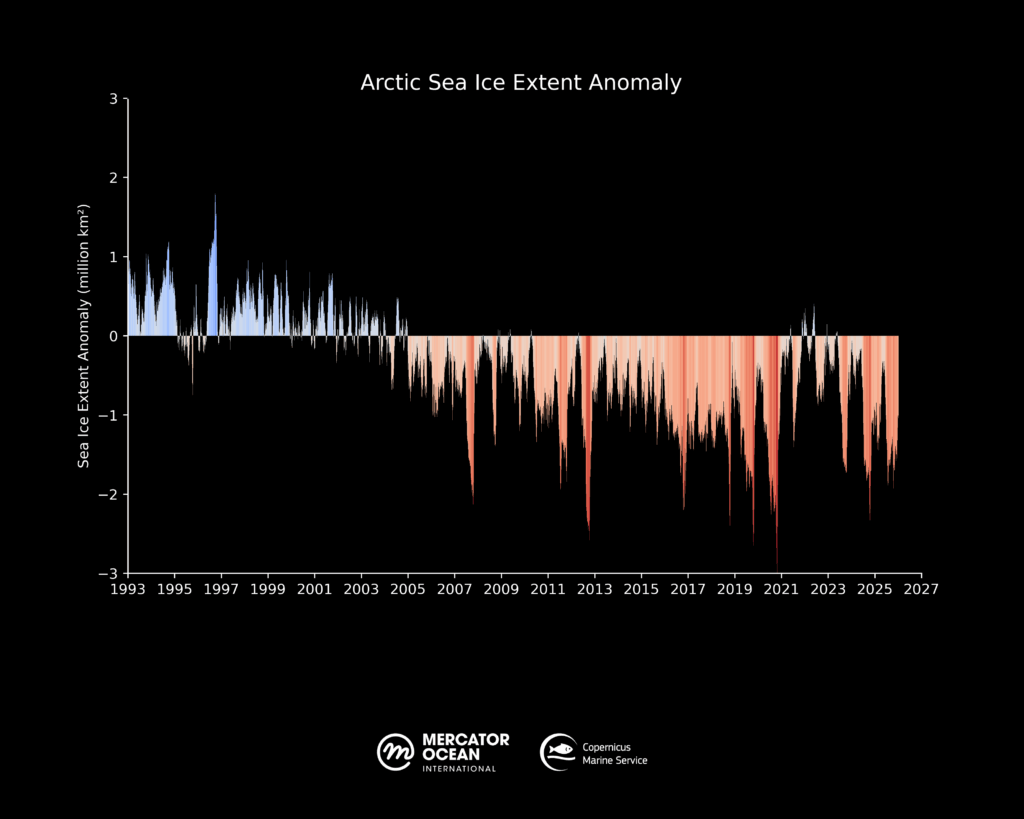
Global sea ice cover in 2025 continued well below the long-term average for most of the year. 11 out of 12 months of the year within the five lowest extents.
Products and data used:
*Image citation: European Union, Copernicus Marine Service Data 2025 I © Mercator Ocean
All images in this article can be used freely and should be cited with the information above.